High-context Cultures Rely More on Nonverbal Cues
Question 4 1 1 pts. B people rely less on the environmental setting to convey meaning.
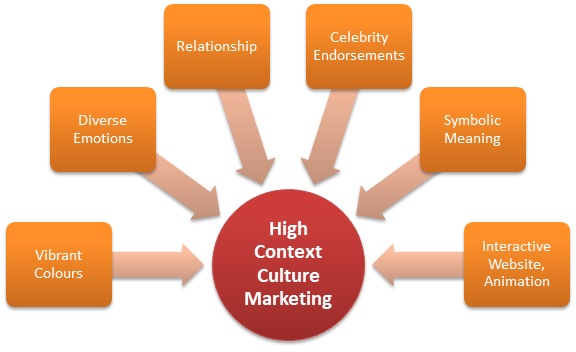
High Context Culture Meaning Importance Example Mba Skool
High context cultures rely more on nonverbal cues than do low context cultures false collectivistic cultures tend to place a high value on self reliance and competition.

. 11 In high-context cultures A people rely more on nonverbal circumstances and cues to convey. High-context cultures rely more on nonverbal cues than do low-context cultures TRUE Mainstream culture in the United States tends to be more low context than high context. 11 In high-context cultures A people rely more on nonverbal circumstances and cues to convey meaning.
Value straight talk and assertiveness. Value and emphasize subtle often nonverbal cues to maintain social harmony b. High-context cultures are those that communicate in ways that are implicit and rely heavily on context.
Question 1 0 1 pts According to Bevan and Sole 2014 high context cultures rely more heavily on nonverbal cues such as body language the situation and environmental factors. People rely less on the environmental setting. C the rules of.
16 Compared to low-context cultures high-context cultures tend to take a ________ approachregarding the meaning of business contracts. A gap in autism research Autism Res. Some cultures called high-context cultures rely heavily on nonverbal and subtle situational cues in communication.
People rely less on the environmental setting to convey meaning C. In high-context cultures such as those in Japan China Korea and Arab countries communication relies heavily on non-verbal contextual and shared cultural meanings. High-context cultures differ from low-context cultures because they.
In anthropology high-context culture and low-context culture are ends of a continuum of how explicit the messages exchanged in a culture are and how important the context is in. 11 In high-context cultures A people rely more on nonverbal circumstances and cues to convey meaning. According to your textbook EVERY interracial encounter is characterized by intercultural communication.
High-context cultures often exhibit less-direct verbal and nonverbal communication utilizing small communication gestures and reading more meaning into these. High-context cultures rely more on nonverbal cues than do low-context cultures. High-context cultures rely more on nonverbal cues than do low- context cultures.
People rely more on nonverbal circumstances and cues to convey meaning B. In high-context cultures A. Cultural differences in social communication and interaction.
True TFEdward Hall found that people in the Middle East stand much closer when conducting. In contrast low-context cultures rely on explicit verbal communication. In high-context cultures a.
Manage cultural barriers to improve communication. Low-context societies rely more on nonverbal cues to reduce uncertainty. C the rules of.
Question 3 1 1 pts According to Bevan high context cultures rely more heavily on nonverbal cues such as body language the situation and environmental factors. Low-context cultures differ from high-context cultures in that low context. 11 In high-context cultures A people rely more nonverbal circumstances and.
High-context cultures rely less on nonverbal cues than do low-context cultures. B people rely less on the environmental setting to convey meaning. Members of high-context cultures dont spend much time getting to know each other before engaging in.
People rely more on nonverbal circumstances and cues to convey meaning. Others called low-context cultures rely more on the words themselves. A less flexible B more literalCmore.

High Context Culture Vs Low Context Culture Communication Design For Avoiding Uncertainty Techtello

High Context And Low Context Cultures Wikiwand
High Context And Low Context Cultures Understanding The Differences

High Context Culture Vs Low Context Culture Communication Design For Avoiding Uncertainty Techtello
No comments for "High-context Cultures Rely More on Nonverbal Cues"
Post a Comment